AI-powered visual inspection uses computer vision AI to analyze machinery, production processes, inventory levels, and workplaces to ensure safe, efficient, and effective business processes. Production lines, heavy machinery, Piston rings, acoustical tiles, aircraft components, pipelines, highway bridges, television panels, contact lenses, printed circuit board assemblies, airport baggage, pharmaceuticals, food products, and workplace safety zones are just a few examples of areas that of the objects that can be monitored and analyzed with AI-powered visual inspection.
Visual inspection is critical to monitoring industrial machinery, transportation infrastructure, manufacturing output, workplace safety, and many other industrial processes. Today human visual inspectors conduct most visual inspections, but manual visual inspection is time-consuming and costly for organizations to deliver.

Many visual inspectors have niche expertise and require specialized training. Organizations worldwide are experiencing workforce shortages, and this labor shortage is driving the cost of visual inspection up even higher. Organizations need to provide products and services at high velocity with few defects, and visual inspection is a bottleneck in many industrial processes.
Computer vision AI automates visual inspection and can detect failures earlier and more effectively than manual human inspection. Visual inspection enhanced by computer vision can reduce equipment failures and maximize operational availability.
AI-powered visual inspection offers many advantages over manual inspection:
As industrial equipment becomes digital and connected, the use of workers doing visual inspections is declining in favor of automated means. A large percentage of the existing inspection workforce is aging and retiring within five to ten years. Business leaders know that automation and digitization are ways to address labor shortages.
Robotic process automation (RPA) is causing a shift in how people work. Automating industrial processes will cause a seismic change in jobs by reducing repeatable, task-based roles while enhancing and creating new workforce roles. Automation helps workers gain skills, be more productive, and spend more time on higher-value tasks.

For manufacturers, airlines, industrial companies, infrastructure, or any capital-intensive business, timing equipment repair is a fundamental tactical outcome of asset management programs. In many cases, asset downtime can stop or suspend production. Being able to forecast parts, staff, and production downtime positively impacts productivity and reduces costs.
Organizations must improve asset efficiency. To make this happen, they need to evolve beyond “basic” asset management approaches like “run-to-failure” or maintenance based on time intervals and usage metrics (e.g., change your oil every three months or 3,000 miles). They also need to implement safeguards that notify the right people when a piece of equipment needs manual inspection.
Computer vision improves accuracy and precision and speeds inspection times. You decide whether and when to take maintenance actions or make capital improvements by visually inspecting the performance and condition of capital assets.
AI-powered visual inspection enables advanced asset management systems that improve mean time to repair (MTTR), mean time between failures (MTBF), overall equipment effectiveness (OEE), the percentage of planned versus unplanned maintenance events, and preventative maintenance compliance. It helps determine the optimal time to take maintenance actions, estimate or extend the remaining usable life of the equipment, and schedule repairs.
Asset productivity increases of up to 20% are possible, and overall maintenance costs may be reduced by up to 10%. (McKinsey 2020)
The journey from manual review to advanced asset management with AI:
Advanced Asset Management
Basic Asset Management
Anomaly detection plays a growing role in AI-powered visual inspection and has played a crucial role in non-computer vision use cases for a long time. Insider trading prevention, computer security, sensor diagnostics, and structural engineering have leveraged anomaly detection tools for many years.
Anomaly detection helps identify product defects or foreign objects, such as weapons, that should not be in a particular environment. Anomaly detection is vital in AI-powered visual inspection because these tools can detect possible problem areas without explicitly training a model to recognize them ahead of time. Anomaly detection provides users with a general method for visual inspection that checks to see if anything is out of place.
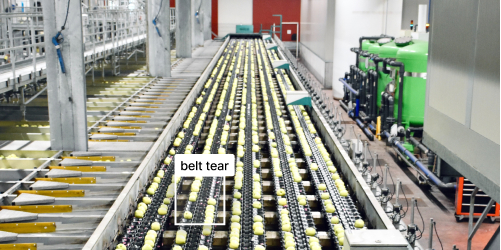 Quality assurance is any systematic way to determine whether a product or service meets specified requirements. Quality assurance prevents mistakes and defects in manufactured products or services to customers and typically deals with quality earlier in the product life cycle. Yield is another critical factor evaluated by quality assurance processes.
Quality assurance is any systematic way to determine whether a product or service meets specified requirements. Quality assurance prevents mistakes and defects in manufactured products or services to customers and typically deals with quality earlier in the product life cycle. Yield is another critical factor evaluated by quality assurance processes.
Automating visual inspection helps manufacturers quickly discover defects in products and services. It’s critical to cutting edge quality assurance efforts in electronics manufacturing such as circuit board components, gluing/-soldiering, product surfaces; semiconductor manufacturing such as wafer inspection, board assembly inspection; and general manufacturing, packaging inspection, labeling inspection, welding inspection.
AI-powered visual inspection systems provide dramatic improvements to production quality inspection and speed. These systems can be deployed anywhere so that manufacturers can spot defects in assets in the field. AI-powered visual inspection systems can send immediate, actionable notifications by email or SMS to help error-proof production.
Gartner believes machine vision quality assurance will be operational in 80% of mass production facilities by 2025, compared with 5% in 2021.
The cost of job injuries and illness is massive, estimated at $250 Billion to $350 Billion per year in the United States. More than 38,000 injuries occur every hour worldwide, and there are nearly 6,000 work-related deaths a day. (ILO 2022)
Computer vision object detection can anonymously identify unsafe human-machine interactions, missing personal protective equipment, mask usage, distracted or fatigued workers, and slips and falls. Real-time alerts can be sent in order to take immediate corrective action.
Beyond reducing lost productivity, workers are provided a safer work environment which leads to reduced workers’ compensation benefit payouts, disability payouts, and a shrinking compensation premium.
 Automating quality testing with AI and advanced image recognition techniques for visual inspection delivers productivity increases of up to 50%. Specifically, AI-based visual inspection based on image recognition may increase defect detection rates by up to 90% compared to human inspection.
Automating quality testing with AI and advanced image recognition techniques for visual inspection delivers productivity increases of up to 50%. Specifically, AI-based visual inspection based on image recognition may increase defect detection rates by up to 90% compared to human inspection.
Collaborative and context-aware robots will improve production throughput based on AI-enabled human-machine interaction in labor-intensive settings. Productivity increases of up to 20% are achievable for specific tasks –even when operations are not fully AI-powered (Gupta, Amaba, McMahon & Gupta 2019).
Clarifai offers a leading computer vision, NLP, and deep learning AI lifecycle architecture for modeling unstructured image, video, text, and audio data. Our technology helps both public sector organizations solve complex use cases through object classification, detection, tracking, geolocation, visual search, and natural language processing. Clarifai offers on-premise, cloud, bare-metal, and classified deployments.
© 2023 Clarifai, Inc. Terms of Service Content TakedownPrivacy Policy






© 2023 Clarifai, Inc. Terms of Service Content TakedownPrivacy Policy